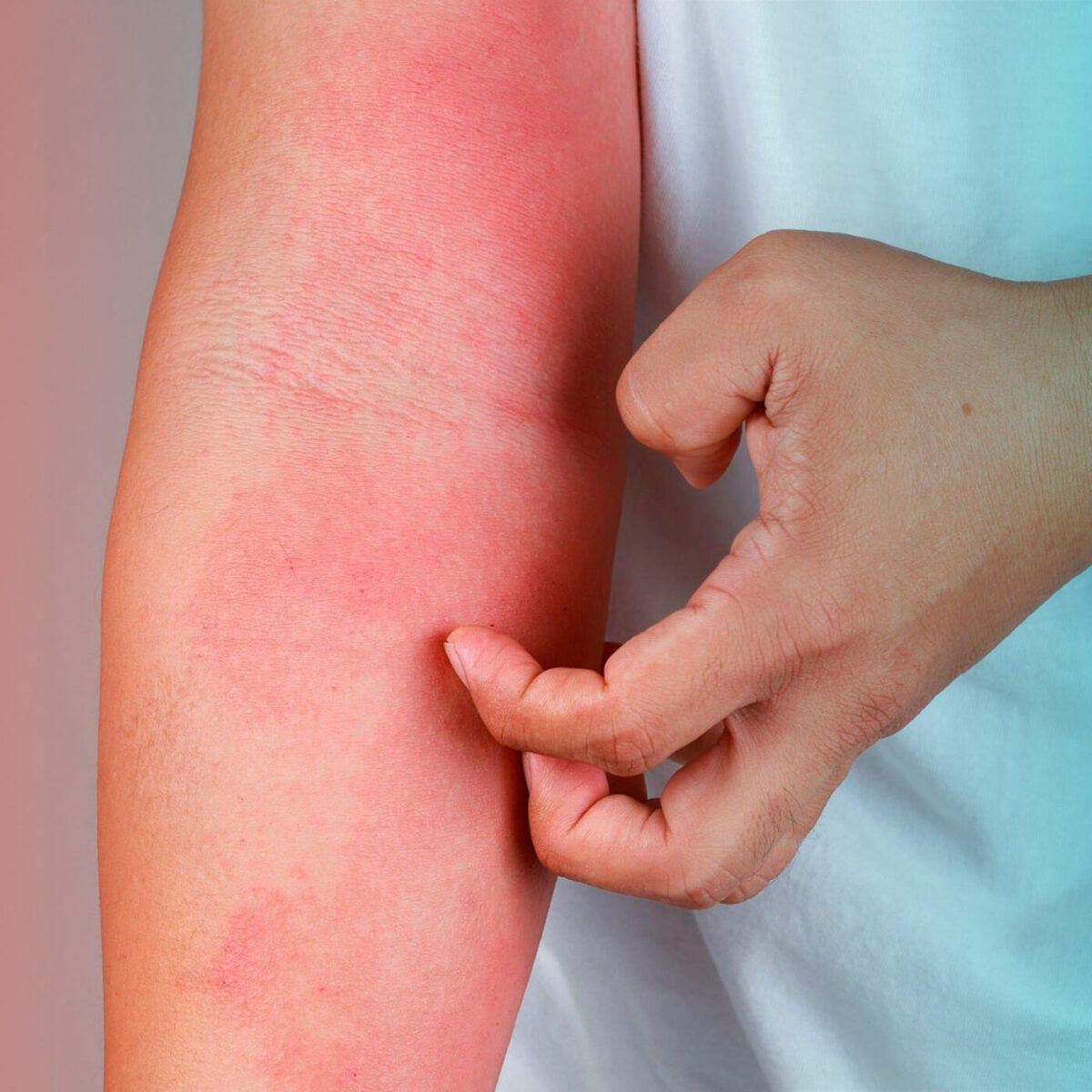
Allergies
Allergies occur when the immune system reacts to certain substances (allergens) as if they were harmful. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, and insect stings. Allergies can lead to symptoms like sneezing, itching, watery eyes, nasal congestion, and skin rashes.
Itchy Eyes
Dust Allergy
Allergies
Hay Fever
OUR PROCESS
Itchy Eyes
Itchy eyes refer to a condition where the eyes experience a persistent itching sensation, often accompanied by redness and irritation. There are several possible causes for itchy eyes, including allergies (such as hay fever or pet allergies), dry eye syndrome, eye infections (such as conjunctivitis or blepharitis), and irritants like dust or smoke. Itchy eyes can also be a symptom of certain systemic conditions or underlying health issues. It is important to avoid rubbing the eyes as it can worsen the irritation and potentially lead to complications. Treatment options for itchy eyes depend on the underlying cause and may include over-the-counter or prescription antihistamine eye drops, lubricating eye drops, cold compresses to soothe the eyes, avoiding known allergens or irritants, and maintaining good eye hygiene. In cases of persistent or severe itching, it is recommended to consult an eye care professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Dust Allergy
A dust allergy refers to an allergic reaction triggered by exposure to dust or particles found in dust. Dust is a common household allergen composed of various substances, including dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, and particles from fabrics or carpets. When a person with a dust allergy comes into contact with these allergens, their immune system reacts by releasing chemicals like histamine, leading to allergy symptoms. Symptoms of a dust allergy can include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and skin reactions like itching or hives. Managing a dust allergy involves minimizing exposure to dust and allergens. This can be done by frequently cleaning and dusting the living environment, using allergy-proof covers for mattresses and pillows, washing bedding in hot water, vacuuming with a HEPA filter, and maintaining low humidity levels to prevent dust mite growth.
Allergies
Allergies are immune system reactions to normally harmless substances. Common types include seasonal allergies, food allergies, and insect sting allergies. Symptoms can include sneezing, itching, runny nose, and skin rashes. Allergies can be diagnosed through medical history, skin tests, or blood tests. Treatment options include avoiding allergens, medications like antihistamines, and immunotherapy. Lifestyle measures like keeping environments clean and carrying emergency epinephrine can help manage allergies. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized management
Hay Fever
Hay fever, also known as allergic rhinitis, is an allergic reaction that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air, particularly during certain seasons. The most common allergens associated with hay fever include pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds, as well as mold spores and dust mites. Symptoms of hay fever can include sneezing, runny or stuffy nose, itchy or watery eyes, itching or irritation in the throat, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Avoiding exposure to allergens, such as staying indoors on high pollen count days or using air filters, can help reduce symptoms. Over-the-counter antihistamines, nasal sprays, and eye drops can provide relief for mild to moderate symptoms. In more severe cases, prescription medications like corticosteroids or immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be recommended. It is advisable to consult with an allergist or healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan for hay fever.