Aches & Pains
OUR PROCESS
Migraine
Migraine is a severe neurological condition characterized by intense headaches, heightened sensitivity to light and sound, as well as symptoms like nausea and vomiting. While the exact cause of migraines remains unclear, genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a significant role. Managing migraines involves a comprehensive approach that includes pain relievers, prescription medications, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies. Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and the development of a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs. By implementing effective management strategies, such as identifying triggers and utilizing appropriate interventions, the frequency and severity of migraine attacks can be significantly reduced, leading to an improved quality of life for those affected. It is important to prioritize self-care and proactive communication with healthcare providers to ensure optimal care and support throughout the migraine journey.
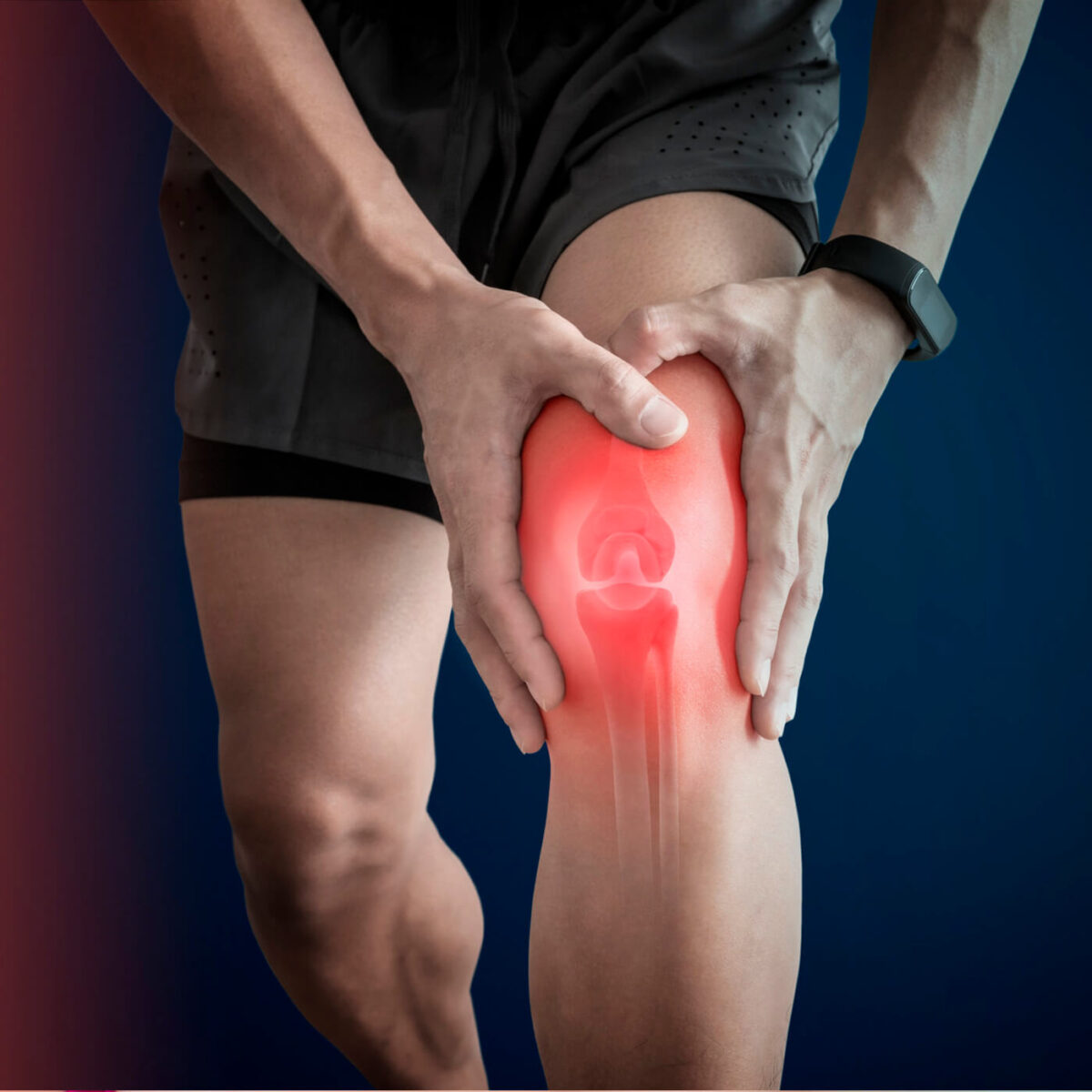
Arthritis
Arthritis refers to a group of conditions characterized by inflammation and stiffness in the joints, resulting in pain and reduced mobility. There are several types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, each with their own causes and symptoms. Common symptoms of arthritis include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. The exact cause of arthritis varies depending on the type but can involve factors such as aging, joint injuries, autoimmune responses, and genetic predisposition. Treatment options for arthritis aim to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function. This may involve medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, assistive devices, and in some cases, surgery. Consulting a healthcare professional is important for an accurate diagnosis and to develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Muscle Sprain
A muscle sprain is an injury that occurs when a muscle or its connecting tendon is stretched or torn. It typically happens due to sudden or excessive force applied to the muscle, such as during sports activities, lifting heavy objects, or sudden movements. Symptoms of a muscle sprain include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the affected muscle or joint. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) is often the initial treatment approach, which involves resting the injured muscle, applying ice packs, compressing the area with a bandage, and elevating the limb to reduce swelling. Over-the-counter pain medications can help manage pain and inflammation. As the sprained muscle heals, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, may be recommended to restore flexibility and regain strength. It is essential to seek medical attention for severe sprains or if symptoms persist, as more serious muscle or tendon damage could be present.
Back Pain
Back pain refers to discomfort or pain felt in the area of the back, ranging from the upper to lower back. It is a common condition that can be caused by various factors, including muscle strains, poor posture, herniated discs, spinal abnormalities, and injury. Symptoms of back pain can vary in intensity and may include aching, stiffness, sharp or shooting pain, limited range of motion, and muscle spasms. Treatment options for back pain depend on the underlying cause and may include rest, physical therapy, pain medications, hot or cold therapy, gentle exercises, and lifestyle modifications such as maintaining proper posture, regular exercise, and weight management. In some cases, medical interventions like injections or surgery may be necessary. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific condition.
Tension Headache
A tension headache is a common type of headache characterized by a dull, aching pain or pressure sensation that typically affects both sides of the head. It is often described as a tight band or pressure around the forehead or the back of the head and neck. Tension headaches are commonly associated with stress, anxiety, muscle tension, and poor posture. Other potential triggers include lack of sleep, eye strain, dehydration, and certain foods. Symptoms of a tension headache may also include sensitivity to light or sound, mild nausea, and difficulty concentrating. Treatment options for tension headaches include over-the-counter pain relievers, rest, stress reduction techniques, applying heat or cold to the affected area, improving posture, regular exercise, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule. In some cases, prescription medications or alternative therapies such as acupuncture or relaxation techniques may be recommended. If tension headaches become frequent or significantly interfere with daily activities, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.